Pipeline configuration¶
Splittting and Merging tasks¶
In CloudConductor, a large task can be processed as multiple smaller tasks using splitters and mergers. In order to define a splitter and merger, please follow the instructions specified in module creation from developer’s guide.
An example use for splitters and mergers is processing the sequencing reads. The input sequencing reads can be aligned independently, thus the aligning procedure can run in parallel. For example, consider the simple pipeline presented in Figure 2.
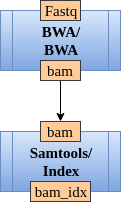
The graph configuration file for the pipeline presented in Figure 2 is:
[align_reads]
module=BWA
final_output=bam
[bam_indexing]
module=Samtools
submodule=Index
docker_image=Samtools_docker
input_from=align_reads
final_output=bam_idx
However, after implementing a .fastq file splitter and a .bam file merger, the new pipeline can be changed as presented in Figure 3.
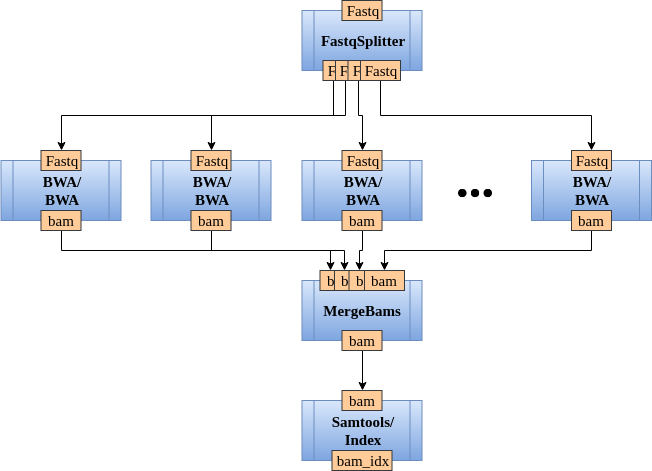
… and the final graph configuration file becomes:
[split_reads]
module=FastqSplitter
[align_reads]
module=BWA
input_from=split_reads
[merge_align]
module=MergeBams
input_from=align_reads
final_output=bam
[bam_indexing]
module=Samtools
submodule=Index
docker_image=Samtools_docker
input_from=align_reads
final_output=bam_idx
As you can observe, in the pipeline definition the new splitter and merger have been added as simple modules. An important thing to notice is that the final_output has been moved from align_reads to merge_align. If the final_output was declared at the level of align_reads, a set of all splitted alignments (not the final merged result) will be considered as final alignment result.
Additional configurationg for a pipeline¶
There are cases when in a specific pipeline run the user wants to override a setting (most times a constant) in a tool.
You can do that as well in the pipeline graph using the args subsection.
For example, let’s say we would like to override the default value of the constants MINLEN and SLIDINGWINDOW_SIZE from Trimmomatic.
In this case, the pipeline graph looks as following:
[trim_reads]
module=Trimmomatic
docker_image=Trimmomatic_docker
[[args]]
MINLEN=20
SLIDINGWINDOW_SIZE=5
These changes will affect only the CloudConductor runs that use the above pipeline graph.